1.SQL查询
1.1 SQL语句
在报表设计器左边的数据集或是共享数据集,点击“新增”则出现数据集窗口页面选中sql查询如下图:

选择数据源,数据源对应数据库,填写数据集名称,数据集名称不能为空且不能与该报表其他数据集重复,默认程序会智能解析sql。
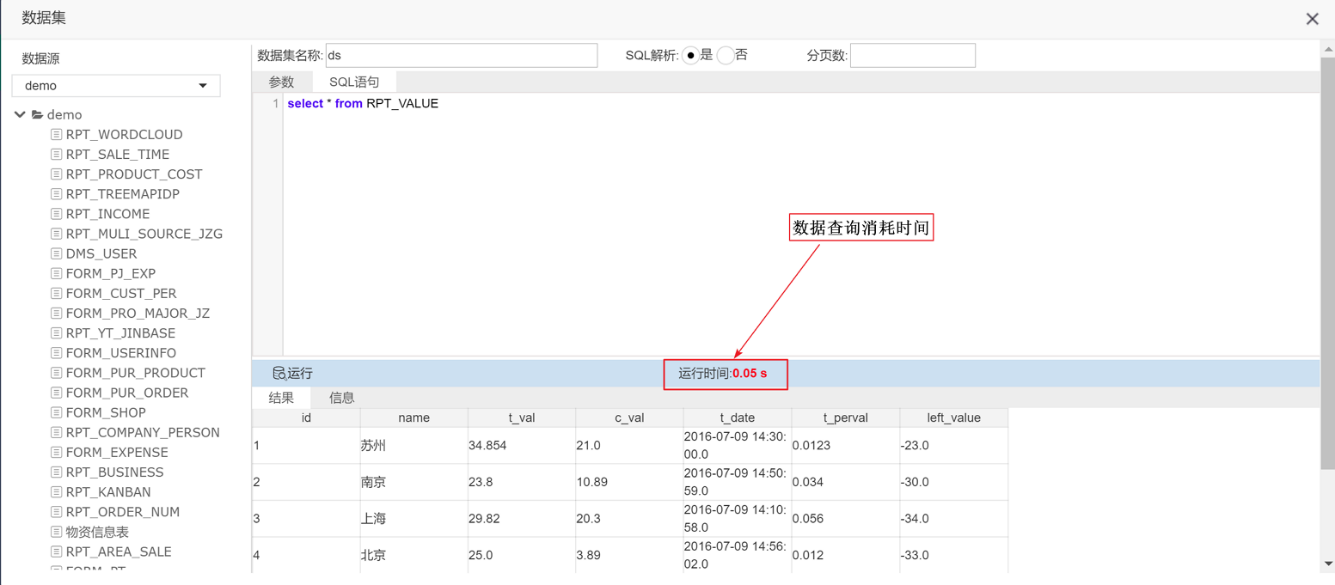
1.2 SQL解析
解析SQL优点
简化带参数的sql语句,如select * from rpt_value where name=:arg, arg为参数名称与参数页面的组件名称相对应,当参数页面不输入arg值即arg为空,sql解析会智能生成可执行的sql语句如:select * from rpt_value where 1=1。
解析SQL缺点
智能解析SQL语句并不能保证解析sql正确性,如果保存sql出现错误,建议SQL解析选择否。
1.3 不解析SQL
SQL解析选择“否”,当sql语句中存在参数,需要写判断参数是否为空的表达式:
select * from rpt_value where 1=1
<if test="arg1 != null"> and name=:arg1</if>
<if test="startDate != null"> and t_date>:startDate</if>
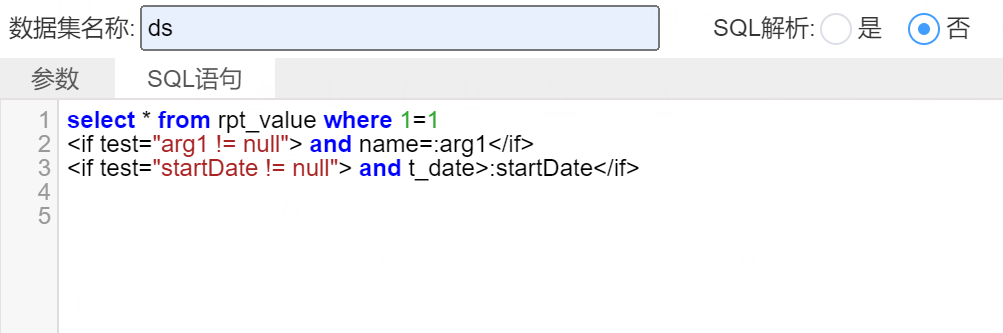
当参数startDate=null,arg = name,生成的可执行的sql:select * from rpt_value where 1=1 and name=’name’
1.4 IF表达式
<if test=""></if>test中为逻辑判断表达式,根据参数最终生成可执行的SQL语句,if表达式也支持嵌套sql判断 示例:可以根据参数sqlType 不同执行不同的SQL语句
<if test="!isdef sqlType">
select * from A
</if>
<if test="sqlType == 'A'">
select * from A where 1=1
<if test="year != null"> and year=:year</if>
</if>
<if test="sqlType == 'B'">
select * from B where 1=1
<if test="year != null"> and year=:year</if>
</if>
if表达式语法:
| 操作符 | 描述 | 示例(argName为参数名称) |
| !isdef | 等于null | isdef 表示是否参数有值, <if test="!isdef argName"></if> |
| isdef | 不等于null | <if test="isdef argName"></if> 或 <if test="argName != null"></if> |
| == | 等于 | <if test="argName == 'A'"></if> |
| != | 不等于 | <if test="argName != 'A'"></if> |
| && | 与,条件均为true,则为true | <if test="argName > 10 && argName < 20"></if> |
| || | 或,条件有一个为ture均为true | <if test="argName > 10 || argName < 5"></if> |
| > | 大于 | <if test="argName > 10"></if> |
| < | 小于 | <if test="argName < 10"></if> |
| <= | 小于等于 | <if test="argName <= 10"></if> |
| >= | 大于等于 | <if test="argName >= 10"></if> |
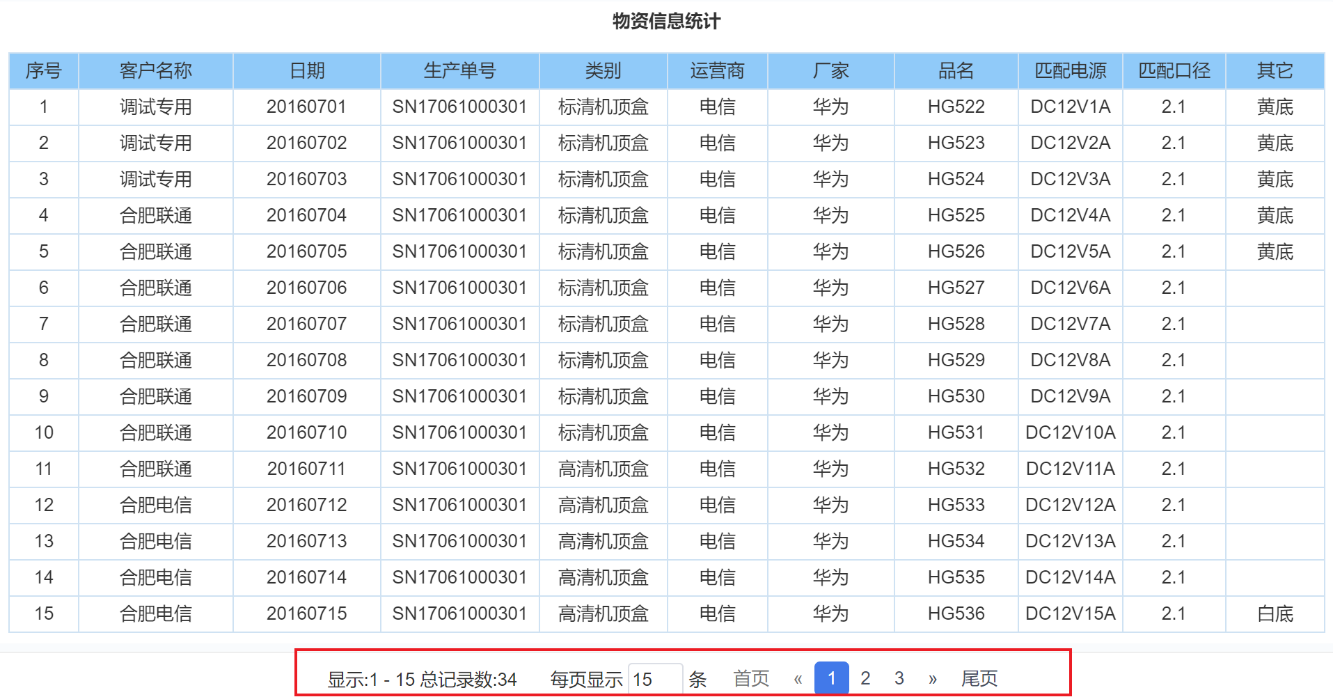
1.5 分页数
分页数为0时表示不使用分页查询,当分页数大于0时,SQL语句在查询时会自动增加SQL分页片段,不需要在SQL检索中写分页查询SQL,当填写分页数如2,程序会智能依据不同数据库添加sql分页片段,如mysql:select * from rpt_value limit 0, 2